

| During much of our time at sea, we will be working with some of the smallest creatures in the ocean: Plankton. The word plankton comes from the Greek word for wanderer (just like the word planet). They are creatures that do not have the ability to swim against a current, and so must drift along with it. The word plankton is used to refer to a variety of different kinds of ocean life that spend part, or all of their life being carried by the ocean currents. Included in the plankton community are tiny plants, small animals, fish that have just hatched, some kinds of bacteria and even jellyfish. Why do we study these creatures? Much of the ocean ecosystem depends on these creatures for food, lives as plankton or both at one point or another in their life. |
 |
|||||||||||
|
Open Source Photo by Uwe Kis
|
||||||||||||
| During our time at sea, we will
be working with instruments called Drifter Buoys. A drifter buoy is an
instrument that floats along in the open sea. It reports its position
and other information to land via satellite link.
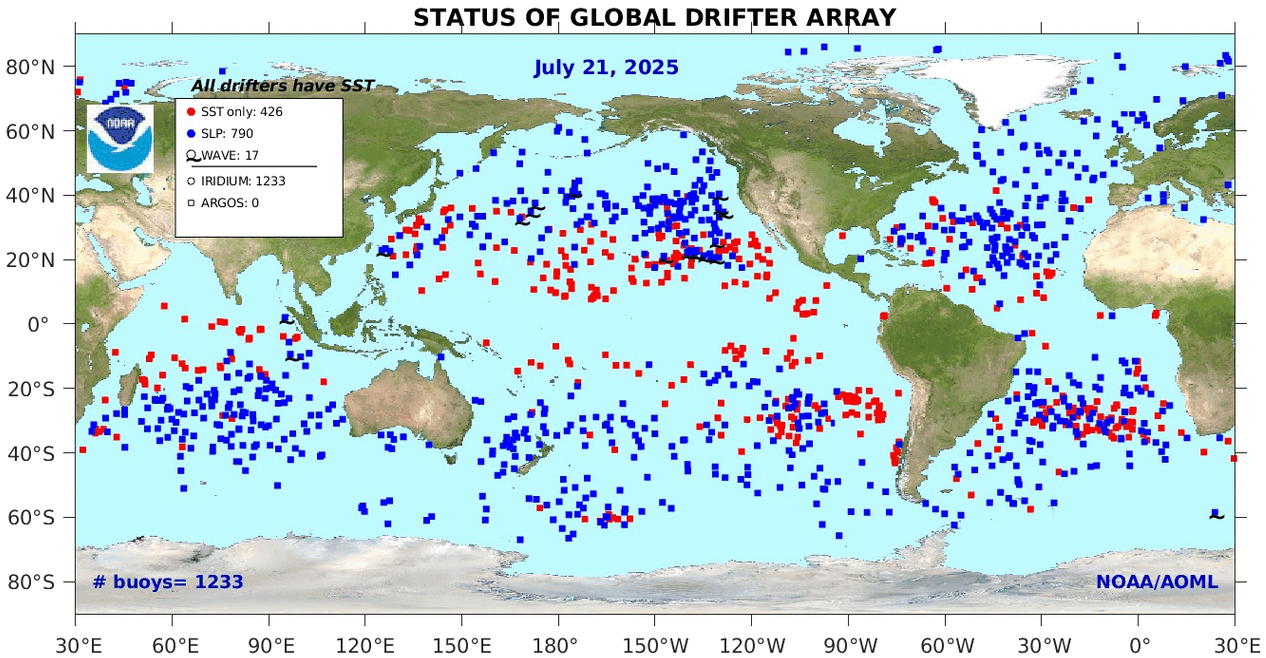
Drifters are an important way that scientists gain understanding of the ocean environment. Drifter buoy data are used in many types of scientific work. Climate scientists, for example, use drifter buoy data when they create the computer models which help us understand how human beings are causing our climate to get warmer. Click the links below to find out more. The NOAA graphic on the right shows the location of each buoy in the global drifter array. You can click on it to expand it for a closer look. |
 |
|||||||||||
Drifter Buoy Links
|
||||||||||||